EYW: Engineering Design and Analysis
Course Overview for EYW: Engineering Design and Analysis
Engineer Your World (EYW): Engineering Design and Analysis is a hands-on, design-based, inquiry-focused engineering course for all learners. In this course, students discover the engineering design process, make data-driven decisions, and work in multi-level teams to solve complex challenges.
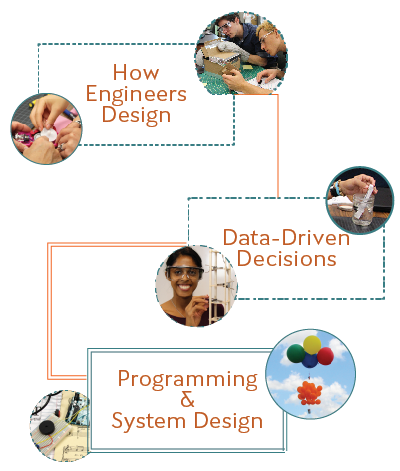
How Engineers Design
Students discover the design process by creating solutions for people with disabilities. They reverse engineer a consumer product to think about how someone else designed it – and how they could do it better.
Data-Driven Decisions
Students uncover the challenges and opportunities of working together to collect, analyze, represent, and argue from data. They use these skills to redesign a building for human safety.
Programming & System Design
Once students know how engineers design and how to make data-driven decisions, they are ready to apply these abilities, along with basic coding skills, to design more complex solutions in a systems engineering capstone challenge.
Request the printable course overview and access sample lessons.
Learn more
Unit Descriptions for EYW: Engineering Design and Analysis
Students explore mechanical, chemical, civil, electrical, and aerospace engineering through a series of design challenges that illustrate how engineering can improve people’s lives and health, meet the special needs of different customer groups, and even enable creativity in the arts.
Unit 1: Pinhole Camera (Discovering Design)
 Pinhole Camera
Pinhole Camera asks students to create solutions for artists with disabilities. Students learn to analyze user needs and interpret requirements for an easy-to-use pinhole camera; employ research-based methods to generate concepts; build, test, and redesign their cameras; and create technical instructions for manufacturers and users. As the teacher guides the students through the project, they ask the class to name the steps of the design process. This constructivist approach empowers students to “own” the process that they will use to solve complex challenges throughout the course.
Unit 2: Flashlight Redesign (Reverse Engineering)
 Custom Flashlight
Custom Flashlight gives students the opportunity to think about how someone else designed a common consumer product, and how they could improve the design. Students identify and interview potential customers; define design requirements and specifications; model and analyze product functionality; generate redesign ideas; and communicate design recommendations.
Unit 3: Calibrated Coffee (Understanding Data)
 Better Coffee
Better Coffee is an “exploration,” a shorter unit that does not require a full iteration of the design cycle and that serves to scaffold particular technical skills for the design challenge that follows. In this unit, students work together as a class to design and conduct an experiment to brew the perfect cup of coffee. Each student analyzes the class-generated data set, considering tradeoffs between speed (a shorter brew time to maximize production) and accuracy (a more controlled brew to improve quality control) before recommending a particular solution and defending that solution based on available data.
Unit 4: Safer Buildings (Data-Driven Design)
 Safer Buildings
Safer Buildings asks students to redesign a building for earthquake resistance. After constructing and testing scale models to uncover the danger of an existing building’s design, students research existing solutions that architectural engineers use in earthquake-prone regions. Using skills developed in the previous unit, students design and conduct an experiment to test building modifications. Each team analyzes the class data set and develops a final design proposal that considers the tradeoffs between building height, cost, and safety; predicts the performance of that design under earthquake conditions; and tests the design. The team’s final report analyzes their design’s performance and, if it failed, explains what went wrong and what steps should be taken next. This ability to “fail forward” is a key skill in engineering – and in life.
Unit 5: Electronic Music (Algorithms and Programming)
 Electronic Music
Electronic Music is an exploration that introduces students to basic electronic circuits and coding by asking them to build a simple speaker circuit and program it to play any piece of music that they like. Students think about the logic of code, explore syntax and structure, and experience the advantages and challenges of visual and text-based integrated development environments.
Unit 6: Aerial Imaging (Engineering Systems)
 Aerial Imaging
Aerial Imaging asks students to create a system to capture images of a disaster zone. Students work together to analyze and decompose the system before dividing into subsystem-level teams to design an electronic payload, a structure to house the payload, and a descent stage to slow the system’s fall. These subsystem teams must work in parallel to accomplish the design challenge while also coordinating to ensure that components will integrate as a system. Teams identify and mitigate risks; select, build, and integrate subsystem designs; and develop and execute launch plans to complete the challenge.
Benefits to Students
EYW: Engineering Design and Analysis expands opportunities for all students by building creative problem-solving and engineering design skills; teaching the value of collaborating to solve complex, modern problems; and creating a strong foundation for future STEM learning.
Students who plan to pursue future engineering studies benefit from learning rigorous design skills and habits of mind and from exploring multiple engineering fields and professions. Those with other plans benefit from learning to think critically and solve complex problems – skills that are useful in any field.
The combination of minimal prerequisites and optional dual enrollment credit allows our first course to be accessible by all students in grades 9-12, while also providing additional layers of difficulty for those seeking an extra challenge.

Learn about dual enrollment
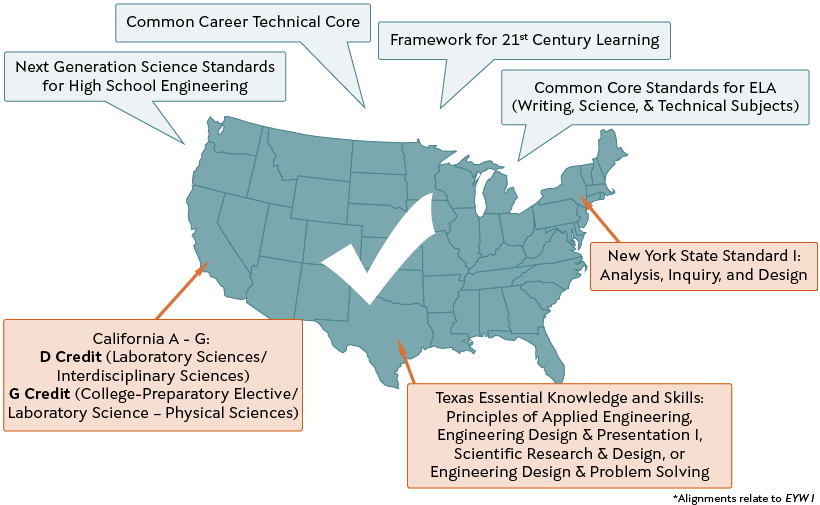
Standards Alignment
Request sample lessons